In recent years, the banking and finance industry has witnessed an increase in mergers and acquisitions, resulting in the need to integrate different IT applications and systems and ensure more efficient and customer-oriented operations.
From data security to employee training: strategies to adopt
As part of their growth strategy, these institutions are merging or acquiring companies around the world, each with their own back-office systems. Organizations are always looking for ways to optimize their IT systems and accelerate the amalgamation of new acquisitions to integrate banking and financial transactional systems into the business ecosystem. Successful integration not only streamlines operations, but also ensures data accuracy, compliance, and efficiency.
Define the goals and strategy for integration
Here are some key considerations for effectively integrating financial transactional systems during mergers and acquisitions.
- Begin with a thorough assessment of both organizations’ financial systems, understanding their architectures, databases, workflows, and regulatory compliance standards.
- Set clear goals for integration, such as consolidating systems, harmonizing processes, or temporarily maintaining separate systems.
- Develop a robust integration strategy aligned with business objectives, defining timelines, milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs).
- It is critical to prioritize data standardization, such as formats, coding structures and naming conventions, to ensure compatibility among systems.
- Investing in data cleansing and deduplication processes improves quality before migration or consolidation.
Unifying IT systems with messaging middleware
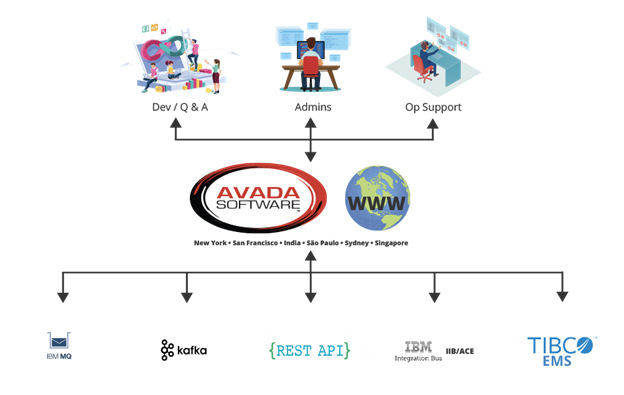
During mergers and acquisitions, organizations often inherit disparate financial systems. Messaging middleware plays a key role in unifying these disparate systems, enabling seamless data flow between legacy systems, ERP, CRM and other transactional platforms. Messaging middleware, such as IBM MQ, Kafka, IBM App Connect Enterprise and others, serves as the backbone to facilitate communication and data transfer between these disparate financial systems within multiple merging entities.
One of its main strengths is its ability to enable real-time data exchange. This ensures that critical financial data, including transactions, account information and operational data, are shared between systems in a timely manner, facilitating informed decision making. Similarly, it is critical that any middleware management and reporting solution be able to provide real-time monitoring, alerting, and administration capabilities.
As the new entity evolves, the inherent scalability of messaging middleware becomes a key element, supporting increasing transaction volumes and system requests and ensuring uninterrupted operations during the growth phase. The messaging architecture must therefore be able to scale effectively, but also adapt to deployment in containerized environments and on various platforms, including cloud and hybrid systems. This adaptability is critical to maintaining performance and efficiency in a rapidly changing technology landscape.
Implementing messaging middleware for financial systems integration requires adherence to best practices. This includes comprehensive planning, establishing data mapping standards, ensuring message reliability, and performing extensive testing to validate seamless data exchange. Ensure that you have effective tools with capabilities to test real (often customized) messages. “Hello World” tests are insufficient to analyze different systems.
Messaging middleware integration must be in line with the strategic vision of all merged entities. It must also be future-ready, allowing for easy integration of new systems or technologies as the organization evolves.
Ensure data security and compliance
In the context of mergers and acquisitions, ensuring data security and compliance is critical. Messaging middleware adds an additional layer of security by providing features such as encryption, authentication and access control to safeguard sensitive financial information and comply with regulatory requirements. From this perspective, it is important:
- Prioritize compliance with industry regulations and data privacy laws throughout the integration process.
- Conduct periodic audits to ensure adherence to standards.
- Constantly monitor integrated systems and the middleware that integrates them for performance, data accuracy, and user feedback.
- Optimize systems based on the information gathered, refining processes and resolving any shortcomings.
Employee training and change management
Providing comprehensive training to employees on new systems and processes allows for a smooth transition, so implementing effective change management strategies to mitigate resistance is critical.
Establishing data ownership and collaboration between business unit employees and IT teams is also essential for rapidly integrating systems from new acquisitions. Data ownership is important to ensure that teams take responsibility for their data, enabling faster troubleshooting in production scenarios. Ad hoc troubleshooting can be challenging when an area includes multiple servers and multiple objects on those servers that need to be changed simultaneously. The situation becomes more complex when it is necessary for someone from the business units to review, interact with, or verify that the proposed changes actually correct the problem.
When another business unit or business leader becomes involved in problem solving, effective collaboration can be indispensable. This can help reduce friction and increase speed, ensuring that companies are more responsive to customers. A collaborative approach to solving merger and acquisition problems is often critical to ensuring the successful integration of new acquisitions into thebusiness ecosystem.
Secure data and team integration with infrared360®
Infrared360®, a Web management portal offered by Orbyta Tech partner Avada Software, provides a middleware management and monitoring solution for companies that want to securely integrate their teams and data, including transactional banking and financial systems integration. The product offers a range of features, such as performance monitoring, testing, auditing, reporting and administration capabilities that enable IT employees to take ownership of their data and collaborate with business units to troubleshoot problems.
In case of problems, such as application failures or messaging object malfunctions, administrators can easily identify and resolve them through an administration portal. This promotes efficient collaboration and ensures smooth integration of newly acquired entities and transactional banking and financial systems.
Role-based access control
Infrared360 ‘s Trusted Spaces feature enables administrators and subject matter experts in the business unit to collaborate effectively by sharing and viewing only the problem environment that affects them. Role-based permissions ensure that the collaborating subject matter expert can only view and not make changes themselves. The solution is made possible by the ability to delegate administration to end users for their own virtual sandboxes, applications, or departmental environments.
Infrared360’s Trusted Spaces allows you to set permissions for individual users or groups of users. These can be categorized by location, application, department or any other criteria needed. By selecting the appropriate options, you can assign a user or group to a specific collection of objects and define a set of permissions or roles that determine what they can see and what actions they can perform with those objects.
Trusted Spaces fosters a truly (orbyta.proactive approachto enterprise messaging by providing secure collaborative solution capabilities for finding alerts and incidents before they become problems. This approach has helped Avada Software customers reduce resolution times and decrease annual hours spent resolving trouble tickets by 90 percent. It allows MQ software to be put in the hands of everyone, regardless of their technical expertise.
Achieve efficient and secure data monitoring
In an organization with many systems working together, effective monitoring of data in total security is critical to quickly identifying and resolving problems. Monitoring and support profiles play a key role in identifying components that belong to specific teams to quickly and effectively resolve problems in a production scenario.
Avada Software not only ensures access to data through secure credentials, but also provides secure monitoring and rules to ensure that sensitive data is protected from unauthorized access. Using Infrared360, organizations can create and manage complex alerts that notify affected personnel to specific business units or applications. This is done without the use of rules engines, scripts or other programs, which helps companies focus on their core activities.
To ensure adequate security, not everyone can have access to sensitive data, and Infrared360® works well with different security measures. It improves visibility and accessibility of interactions and interfaces for employees, contributing to integration among teams and enabling seamless collaboration among members while integrating transactional banking and financial systems.
Condividi tramite